Social vs cultural capital mcat, a concept that has gained significant traction in the medical field, explores the multifaceted relationship between social and cultural factors and their profound impact on health outcomes. This article delves into the key differences between social and cultural capital, their respective roles in medical education and practice, and the interventions that can be employed to foster their growth.
Social capital refers to the networks, relationships, and trust that individuals possess within a community, while cultural capital encompasses the knowledge, skills, and values that are shared within a particular cultural group. Both forms of capital play a crucial role in shaping health outcomes, with social capital facilitating access to resources and support, and cultural capital influencing health beliefs and behaviors.
Social Capital vs. Cultural Capital

Social capital and cultural capital are two important forms of capital that can have a significant impact on an individual’s life chances. Social capital refers to the networks of relationships and trust that individuals have access to, while cultural capital refers to the knowledge, skills, and cultural resources that individuals possess.
Both social capital and cultural capital can be important for success in life. Social capital can help individuals to get jobs, find housing, and access other resources. Cultural capital can help individuals to succeed in school, get better jobs, and earn higher incomes.
Social Capital
Social capital is the sum of the resources, both tangible and intangible, that accrue to individuals and groups by virtue of their membership in social networks or other social structures. It includes such things as trust, reciprocity, information, and social norms.
Social capital can be acquired through a variety of means, including participation in social activities, volunteering, and building relationships with others. It can also be inherited from parents or other family members.
Cultural Capital
Cultural capital is the sum of the knowledge, skills, and cultural resources that an individual possesses. It includes such things as education, language skills, and knowledge of the arts.
Cultural capital can be acquired through a variety of means, including formal education, reading, and travel. It can also be inherited from parents or other family members.
Relative Importance of Social and Cultural Capital
The relative importance of social and cultural capital varies depending on the context. In some contexts, social capital may be more important, while in other contexts, cultural capital may be more important.
For example, in a job market where personal connections are important, social capital may be more important than cultural capital. However, in a job market where specialized skills are required, cultural capital may be more important than social capital.
The Role of Social and Cultural Capital in the Medical Field
Social and cultural capital play significant roles in shaping individuals’ experiences and outcomes within the medical field. Social capital refers to the networks, relationships, and resources that individuals can access through their social connections. Cultural capital, on the other hand, encompasses the knowledge, skills, and values that are valued within a particular society or group.
Social Capital in Medical School and Careers
In medical school, social capital can provide students with access to study groups, mentorship opportunities, and research collaborations. These connections can enhance students’ academic performance, foster professional development, and increase their chances of matching into competitive residency programs.As physicians, social capital can facilitate access to specialized knowledge, resources, and support systems.
Strong relationships with colleagues, patients, and community organizations can improve patient care, promote interdisciplinary collaboration, and enhance career advancement opportunities.
Cultural Capital and Access to Healthcare
Cultural capital influences access to healthcare in several ways. Individuals with higher cultural capital may have a better understanding of the healthcare system, be more comfortable navigating its complexities, and possess the necessary resources to seek appropriate care.Conversely, individuals with lower cultural capital may face barriers in accessing healthcare due to language barriers, lack of health literacy, or cultural beliefs that discourage seeking medical attention.
Interaction of Social and Cultural Capital
Social and cultural capital can interact to shape health outcomes. For example, individuals with strong social networks may be more likely to adopt healthy behaviors, such as regular exercise or a balanced diet, due to the influence of their peers.Additionally,
cultural capital can influence the way individuals interact with healthcare providers. Patients with cultural capital that aligns with the healthcare system’s values and norms may have better communication and rapport with their providers, leading to improved health outcomes.
Interventions to Increase Social and Cultural Capital: Social Vs Cultural Capital Mcat
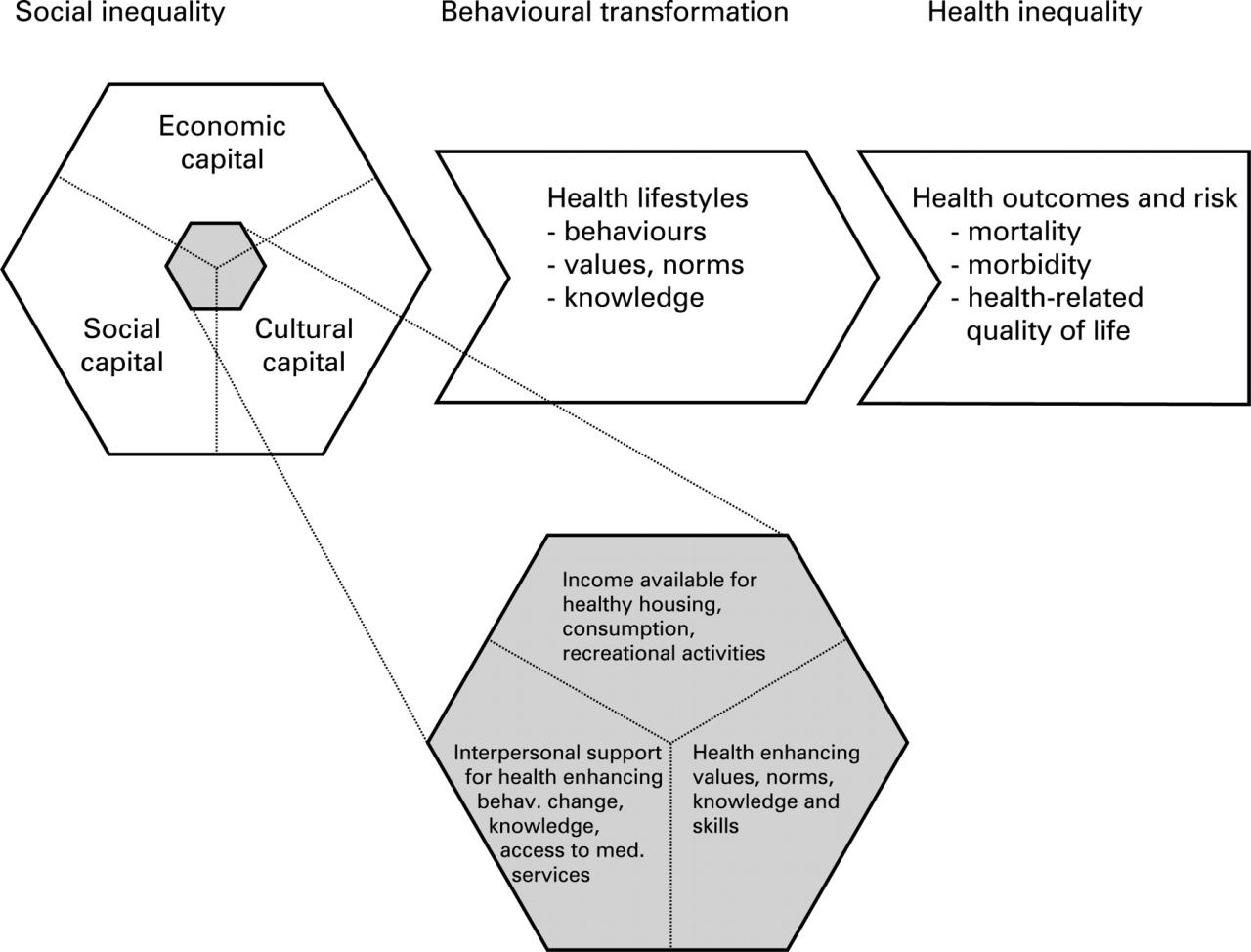
Interventions to increase social and cultural capital among medical students and physicians are crucial for promoting health equity and improving patient outcomes. These interventions aim to foster a sense of community, belonging, and support within the medical field, empowering individuals to navigate the complexities of healthcare systems and advocate for their patients’ needs.
Mentoring and Networking Programs
Mentoring and networking programs provide opportunities for medical students and physicians to connect with experienced professionals who can offer guidance, support, and career advice. These programs facilitate the exchange of knowledge, skills, and perspectives, fostering a sense of belonging and reducing feelings of isolation.
Community Engagement Initiatives
Community engagement initiatives involve medical students and physicians in activities that directly benefit the communities they serve. By working alongside community members, healthcare professionals gain a deeper understanding of the social and cultural factors that influence health outcomes. This engagement builds trust, fosters collaboration, and empowers communities to advocate for their own health.
Diversity and Inclusion Training
Diversity and inclusion training programs aim to raise awareness about the importance of diversity and inclusion in healthcare. These programs educate participants on the biases and barriers faced by marginalized groups and provide tools to create more equitable and inclusive environments.
By promoting empathy and understanding, these trainings foster a culture of respect and collaboration.
Advocacy and Leadership Development
Advocacy and leadership development programs equip medical students and physicians with the skills and knowledge necessary to advocate for health equity and social justice. These programs provide training on policy analysis, communication strategies, and coalition-building, empowering individuals to use their voices to influence change and improve health outcomes for underserved populations.
Future Directions for Research on Social and Cultural Capital in Medicine
Research on social and cultural capital in medicine is still in its early stages, but it has the potential to make a significant contribution to our understanding of health and healthcare. Future research should focus on several key areas, including:
Measuring social and cultural capital
There is a need for more research on how to measure social and cultural capital. This will help researchers to track changes in social and cultural capital over time and to identify the factors that are associated with these changes.
The relationship between social and cultural capital and health outcomes
Research is needed to explore the relationship between social and cultural capital and health outcomes. This research should examine how social and cultural capital can influence health behaviors, access to healthcare, and the quality of healthcare.
Interventions to increase social and cultural capital
Research is needed to develop and evaluate interventions to increase social and cultural capital. These interventions could be targeted at individuals, families, or communities.
The potential implications of this research for improving health outcomes are significant. By increasing our understanding of social and cultural capital, we can develop more effective interventions to improve health and healthcare.
Recommendations for future research studies, Social vs cultural capital mcat
Future research studies should focus on the following areas:
- Developing and validating measures of social and cultural capital
- Exploring the relationship between social and cultural capital and health outcomes
- Developing and evaluating interventions to increase social and cultural capital
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between social capital and cultural capital?
Social capital refers to the networks, relationships, and trust that individuals possess within a community, while cultural capital encompasses the knowledge, skills, and values that are shared within a particular cultural group.
How does social capital impact health outcomes?
Social capital can facilitate access to resources and support, such as healthcare services, information, and emotional support, which can all contribute to improved health outcomes.
What are some examples of interventions that can increase social capital?
Examples of interventions that can increase social capital include community-based programs that promote social interaction and support, such as mentorship programs, peer support groups, and neighborhood watch programs.