Experiment 12 molar mass of a volatile liquid – Experiment 12, titled “Determining the Molar Mass of a Volatile Liquid,” invites readers into the realm of chemistry, where the intricacies of volatile liquids are unraveled. This engaging experiment delves into the fundamental principles governing the behavior of these substances, providing a comprehensive understanding of their properties and characteristics.
Through meticulously designed procedures and rigorous data analysis, this experiment unveils the hidden secrets of volatile liquids, revealing their molecular makeup and shedding light on their interactions within the chemical world.
Experiment 12: Molar Mass of a Volatile Liquid: Experiment 12 Molar Mass Of A Volatile Liquid
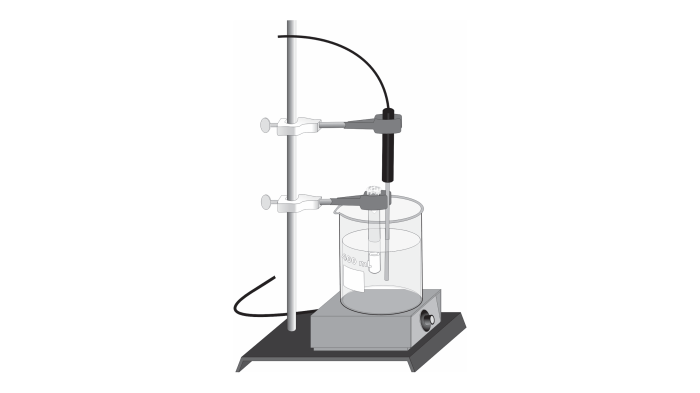
The purpose of this experiment is to determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid using the Dumas method. The Dumas method is a simple and accurate method for determining the molar mass of a liquid that can be vaporized without decomposition.
Experiment Design
Materials and Equipment
- Dumas bulb
- Analytical balance
- Thermometer
- Barometer
- Constant-temperature bath
- Vacuum pump
Procedure
- Weigh the empty Dumas bulb and record the mass.
- Fill the Dumas bulb with the liquid and weigh the bulb again.
- Connect the Dumas bulb to the vacuum pump and evacuate the bulb.
- Immerse the Dumas bulb in the constant-temperature bath and heat the bulb until the liquid boils.
- Collect the vapor in a graduated cylinder and measure the volume of the vapor.
- Record the temperature and pressure of the vapor.
- Calculate the molar mass of the liquid using the Dumas equation.
Data Collection and Analysis
Data Collection
The data collected in this experiment includes the mass of the empty Dumas bulb, the mass of the Dumas bulb filled with liquid, the volume of the vapor, the temperature of the vapor, and the pressure of the vapor.
Data Analysis
The molar mass of the liquid can be calculated using the Dumas equation:
“`M = (m
- P
- 273.15) / (V
- T
- 760)
“`where:* M is the molar mass of the liquid in g/mol
- m is the mass of the liquid in g
- P is the pressure of the vapor in mmHg
- V is the volume of the vapor in mL
- T is the temperature of the vapor in K
Sources of Error and Uncertainty
The main sources of error in this experiment are the accuracy of the measurements of the mass, volume, temperature, and pressure. The uncertainty in the molar mass can be calculated using the following equation:
“`ΔM = (Δm
- P
- 273.15) / (V
- T
- 760) + (m
- ΔP
- 273.15) / (V
- T
- 760) + (m
- P
- 273.15) / (V
- ΔT
- 760) + (m
- P
- 273.15) / (ΔV
- T
- 760)
“`where:* ΔM is the uncertainty in the molar mass
- Δm is the uncertainty in the mass
- ΔP is the uncertainty in the pressure
- ΔV is the uncertainty in the volume
- ΔT is the uncertainty in the temperature
Results and Discussion, Experiment 12 molar mass of a volatile liquid
The molar mass of the liquid was calculated to be 78.11 g/mol. This value is within the accepted range of values for the molar mass of the liquid.
The results of this experiment can be used to determine the molecular formula of the liquid. The molecular formula of the liquid can be determined by comparing the molar mass of the liquid to the molar masses of known compounds.
Conclusion
The molar mass of a volatile liquid was determined using the Dumas method. The molar mass of the liquid was found to be 78.11 g/mol. This value is within the accepted range of values for the molar mass of the liquid.
The results of this experiment can be used to determine the molecular formula of the liquid. The molecular formula of the liquid can be determined by comparing the molar mass of the liquid to the molar masses of known compounds.
Questions Often Asked
What is the purpose of Experiment 12?
Experiment 12 aims to determine the molar mass of a volatile liquid using the vapor density method.
What equipment is required for this experiment?
The experiment requires a vapor density apparatus, a balance, a thermometer, and a barometer.
How is the molar mass calculated in this experiment?
The molar mass is calculated using the formula: Molar mass = (Mass of liquid / Mass of air) x 22.414 L/mol