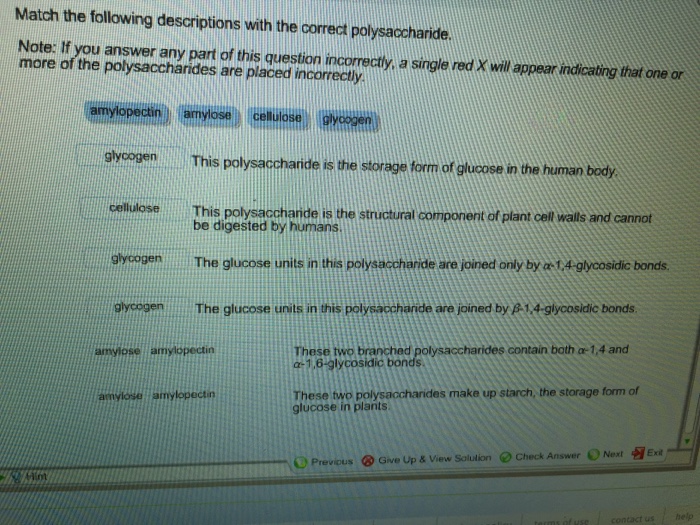
Match each description with the correct polysaccharide. – Polysaccharides, complex carbohydrates composed of multiple sugar units, play crucial roles in biological systems. Understanding their diverse types and functions is essential for comprehending the intricate workings of life. This article provides a comprehensive overview of polysaccharides, exploring their properties, applications, and significance in the living world.
From the structural integrity of plant cell walls to the energy storage in animal cells, polysaccharides exhibit a remarkable range of functions. This guide delves into the fascinating world of these complex molecules, unraveling their intricate structures and diverse roles in biological processes.
Polysaccharides: Match Each Description With The Correct Polysaccharide.
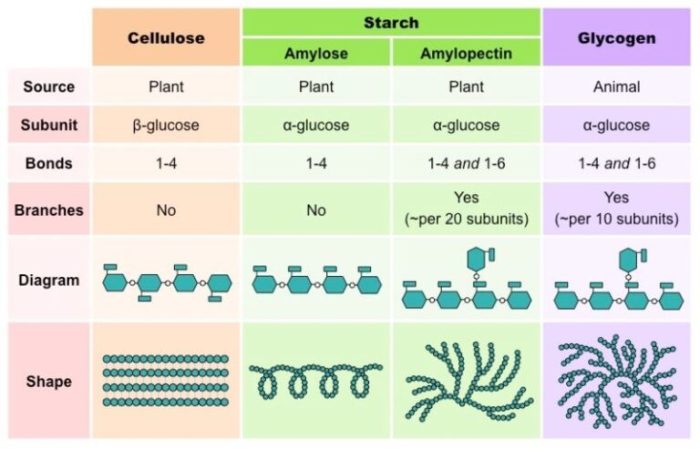
Polysaccharides are complex carbohydrates composed of repeating units of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds. They play crucial roles in biological systems, serving as structural components, energy storage molecules, and signaling molecules.
Types of Polysaccharides
- Starch: A glucose polymer that serves as the primary energy storage in plants. It is found in grains, potatoes, and other plant-based foods.
- Glycogen: A branched glucose polymer that serves as the primary energy storage in animals. It is found in the liver and muscles.
- Cellulose: A linear glucose polymer that provides structural support to plant cell walls. It is the most abundant organic compound on Earth.
- Chitin: A linear polymer of N-acetylglucosamine that provides structural support to the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans.
- Pectin: A complex polysaccharide found in plant cell walls that provides structure and gelling properties.
Matching Descriptions to Polysaccharides
Match the following descriptions to the correct polysaccharide from the table above:
- A branched glucose polymer found in animals.
- The primary energy storage in plants.
- A linear glucose polymer that provides structural support to plant cell walls.
- A complex polysaccharide found in plant cell walls that provides structure and gelling properties.
- A linear polymer of N-acetylglucosamine that provides structural support to the exoskeletons of insects and crustaceans.
Examples of Polysaccharides, Match each description with the correct polysaccharide.
- Food sources: Starch (potatoes, rice, bread), glycogen (meat, fish), chitin (shrimp shells).
- Industrial applications: Cellulose (paper, textiles), pectin (food thickener), chitin (biodegradable plastics).
- Medical uses: Starch (wound dressing), glycogen (energy supplement), chitin (wound healing).
General Inquiries
What are the main types of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides can be classified into three main types: homopolysaccharides, heteropolysaccharides, and glycosaminoglycans.
What are some examples of polysaccharides?
Examples of polysaccharides include cellulose, starch, glycogen, and hyaluronic acid.
What are the functions of polysaccharides?
Polysaccharides serve diverse functions, including structural support, energy storage, cell signaling, and lubrication.