What problem-solving strategies are essentially mental shortcuts? This question opens up a fascinating realm where cognitive strategies converge to simplify complex challenges and unlock creative solutions. By delving into the depths of cognitive shortcuts, pattern recognition, and other techniques, we embark on a journey to understand how our minds navigate the intricate landscapes of problem-solving.
Throughout this exploration, we will uncover the advantages and limitations of using heuristics, examine the role of pattern recognition in enhancing cognitive efficiency, and explore how simplification and abstraction can make complex problems more manageable. Furthermore, we will investigate the power of analogy and metaphor as problem-solving tools, delve into the significance of mental simulation and visualization, and appreciate the importance of trial and error in iterative refinement.
What Problem-Solving Strategies Are Essentially Mental Shortcuts?
Problem-solving is a crucial cognitive process that involves finding solutions to challenges or obstacles. To simplify this process, individuals often rely on mental shortcuts, which are cognitive strategies that expedite problem-solving.
Cognitive Shortcuts and Heuristics
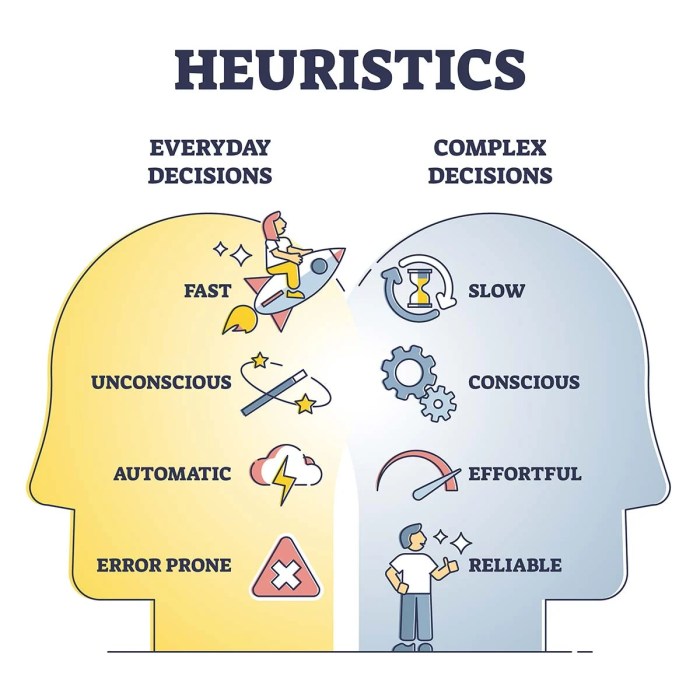
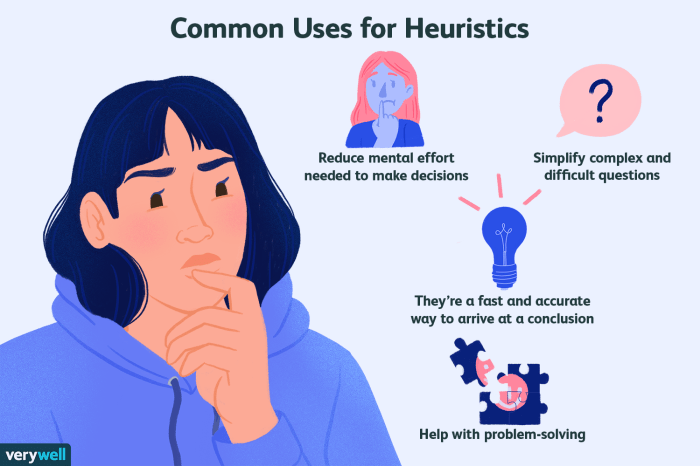
Mental shortcuts, also known as heuristics, simplify problem-solving by reducing the cognitive effort required. Heuristics provide quick and efficient solutions, but they can also introduce biases or inaccuracies.
- Advantages:Speed, efficiency, and reduced cognitive load.
- Limitations:Potential for bias, overgeneralization, and errors.
- Examples:Representativeness heuristic, availability heuristic, and anchoring bias.
Pattern Recognition and Chunking, What problem-solving strategies are essentially mental shortcuts
Pattern recognition plays a vital role in problem-solving by identifying familiar patterns and applying learned solutions. Chunking, or grouping information into smaller units, enhances cognitive efficiency and memory recall.
- Techniques:Identifying patterns, breaking down information into manageable chunks, and using mnemonic devices.
Simplification and Abstraction
Simplification involves reducing the complexity of a problem by focusing on its essential elements. Abstraction involves representing a problem at a higher level of generalization, ignoring irrelevant details.
- Benefits:Makes problems more manageable, reduces cognitive load, and fosters creativity.
- Techniques:Removing unnecessary information, using models or diagrams, and focusing on key concepts.
Analogy and Metaphor
Analogy and metaphor are powerful tools for problem-solving by drawing parallels between different situations. They foster creativity and provide fresh perspectives.
- Benefits:Stimulate creative thinking, enhance understanding, and provide new insights.
- Examples:Using the human body as an analogy for a computer system or comparing a business strategy to a military campaign.
Mental Simulation and Visualization
Mental simulation involves creating a mental model of a problem and testing potential solutions. Visualization involves forming a mental image of a solution or outcome.
- Benefits:Enhances problem comprehension, facilitates solution generation, and improves decision-making.
- Techniques:Creating mental models, using diagrams or sketches, and practicing mental visualization exercises.
Trial and Error and Iterative Refinement
Trial and error is a straightforward approach that involves attempting different solutions until a satisfactory outcome is found. Iterative refinement involves making incremental improvements to a solution until it meets the desired criteria.
- Benefits:Can lead to novel solutions, promotes flexibility, and encourages experimentation.
- Techniques:Generating multiple solutions, testing each solution, and refining based on feedback.
Lateral Thinking and Divergent Approaches
Lateral thinking involves approaching problems from unconventional angles, breaking away from traditional思维 patterns. Divergent thinking encourages generating multiple, diverse solutions to a problem.
- Benefits:Fosters creativity, challenges assumptions, and leads to innovative solutions.
- Techniques:Brainstorming, mind mapping, and role-playing.
Emotional Regulation and Stress Management
Emotions can significantly impact problem-solving. Managing stress and regulating emotions is crucial for maintaining cognitive clarity and making sound decisions.
- Techniques:Mindfulness, relaxation exercises, and stress management strategies.
Question & Answer Hub: What Problem-solving Strategies Are Essentially Mental Shortcuts
What are the benefits of using mental shortcuts in problem-solving?
Mental shortcuts can simplify complex problems, reduce cognitive load, and speed up the problem-solving process.
How does pattern recognition contribute to problem-solving?
Pattern recognition allows us to identify similarities and relationships in problems, enabling us to apply known solutions or adapt existing strategies.
Can mental shortcuts lead to errors in problem-solving?
While mental shortcuts can be helpful, they can also lead to errors if they are applied blindly or without considering the specific context of the problem.